4 条题解
-
3
Sky1231 (sky1231) LV 10 @ 2018-01-26 22:14:31
#include <cmath> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <cstring> #include <iomanip> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> #include <deque> #include <set> #include <limits> #include <string> #include <sstream> using namespace std; namespace dts { typedef long long ll; //splay ll size; ll fa[3000000+1]; ll s[3000000+1][1+1]; ll sl[3000000+1]; ll sr[3000000+1]; ll len[3000000+1]; //splay struct splay { ll root; ll insert(ll l,ll r) { size++; fa[size]=s[size][0]=s[size][1]=0; len[size]=(sr[size]=r)-(sl[size]=l); //interval [l,r) [l,r-1] return size; } ll pr(ll l,ll r) { return (root=insert(l,r)); } ll update(ll now) { return (len[now]=len[s[now][0]]+len[s[now][1]]+sr[now]-sl[now]); } ll dir(ll now) { //left or right return ((s[fa[now]][1]==now)?1:0); } void rotate(ll now) { ll nowdir=dir(now),nowfa=fa[now]; fa[now]=fa[nowfa]; if (nowfa==root) root=now; else s[fa[nowfa]][dir(nowfa)]=now; if ((s[nowfa][nowdir]=s[now][nowdir^1])!=0) fa[s[nowfa][nowdir]]=nowfa; fa[s[now][nowdir^1]=nowfa]=now; update(nowfa); update(now); } void splay_work(ll now) { for (;fa[now];rotate(now)) if (fa[fa[now]]!=0) rotate((dir(now)==dir(fa[now]))?fa[now]:now); } ll split(ll now,ll x) { x+=sl[now]; //pre x number not change //behind number move to new node ll ans=insert(x,sr[now]); //ans new node sr[now]=x; if (s[now][1]==0) fa[s[now][1]=ans]=now; else { ll t; //t temp for (t=s[now][1];s[t][0]!=0;t=s[t][0]) ; fa[s[t][0]=ans]=t; for (;t!=now;t=fa[t]) update(t); } splay_work(ans); return ans; } ll pop(ll x) { //pop x th number ll now,flag; for (now=root,flag=1;flag;) if (len[s[now][0]]>=x) now=s[now][0]; else { x-=len[s[now][0]]; if (x<=sr[now]-sl[now]) { if (x!=sr[now]-sl[now]) split(now,x); if (x!=1) now=split(now,x-1); flag=0; } else { x-=sr[now]-sl[now]; now=s[now][1]; } } splay_work(now); //delete fa[s[now][0]]=fa[s[now][1]]=0; if (s[now][0]==0) root=s[now][1]; else { ll t; //t temp for (t=s[now][0];s[t][1]!=0;t=s[t][1]) ; splay_work(t); update(root=fa[s[t][1]=s[now][1]]=t); } return sl[now]; } ll push_back(ll x) { //push back number x ll ans=insert(x,x+1); if (root==0) return (root=ans); else { ll now; for (now=root;s[now][1]!=0;now=s[now][1]) ; splay_work(now); update(fa[s[now][1]=ans]=now); return ans; } } }; splay sp[300000+1]; void main() { ll n,m,q; scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&n,&m,&q); size=0; for (ll i=1;i<=n;i++) sp[i].pr((i-1)*m+1,i*m); sp[0].pr(m,m+1); for (ll i=2;i<=n;i++) sp[0].push_back(i*m); for (ll i=1;i<=q;i++) { ll x,y,temp; scanf("%lld%lld",&x,&y); sp[x].push_back(sp[0].pop(x)); printf("%lld\n",temp=sp[x].pop(y)); sp[0].push_back(temp); } } }; int main() { dts::main(); } -
1@ 2019-07-02 20:02:59
纯树状数组解法 6500MS过的,最慢的点是1000MS,应该是稳的。
pre:\ 这最后的20%确实挺有难度的,有不少的细节,如果我是去正式比赛,我应该还是拿前80%稳妥一点...
然后写完瞅了眼大家的题解,呃,思路应该是差不多的,不过可能有几份题解讲的还不够详细。这里稍微总结一下。
main:\ 看到题目首先想100%的做法,想10分钟,一点思路都没有,开始看局部分。
测试点1 - 6 30%
完全是送分,直接暴力就行了,这个就不详细说了
测试点7 - 10 20%
n和m增大,存不下这么多数据了。一开始我没什么思路,先想的后面的数据,不过后面想完,回过头一下就想出来了,为了使得大家更好理解为什么会这样,大家可以先看下面。
测试点11 - 16 30%
15和16 2个点就n变大了而已,由于x = 1,所以除了第一行,后面的n全是浪费空间,根本不用管的,所以11 - 16测试点完全可以用同一个算法。
那么仔细观察这个列队操作,我们发现,会产生变化的只有第一行和最后一列。
先考虑这个最后一列,把它单独拿出来,对于每次操作,相当于把这个一列的最上面这个数字丢到第一行,然后把删掉的这个数字给插入到这一列的末尾。
仔细想想,这不就一队列的基本操作么??先进先出,所以直接拿一个队列维护这一列就好了。
然后考虑怎么维护这一行,有点麻烦,如果我们暴力,查询是O(1),修改是O(n),如果改成链表,反过来,总复杂度还是O(qn),太大了。
我们猜,应该可以有查询和修改都是log级别的做法。又是线段,然后很自然的想到线段树和树状数组,或者一些查找树之类的。
一开始我想到的是,拿树状数组维护差分数组搞,搞了一会没法推公式,放弃这个想法了。
然后刚好想到CF上以前做过的一道题!发现两者是一样的\ CF-978C
原本的操作(1,4)表示删除第1行第4个数字,我们把它的含义稍微修改一下,操作(1,4)表示,删除第1行第4个还未被删除的数字。
这样想有什么用呢?我们拿一个数组,一开始都是1,表示没删除,删除以后改成0(这部分是单点修改),然后,前缀和(这部分是区间修改)等于4的点是不是就我们要的答案?而且可以很轻松的想到,这个点有且仅有一个。
显然这个前缀和是单调不减的,因此直接可以2分找到那个位置!!
单点修改,区间查询,树状数组基本操作,加上二分,复杂度qlogmlogm!,这部分分到手了!
然后回过头想7 - 10测试点,显然右边那一列我们得单独拿出来讨论,这在刚才我们已经发现了,因为这一列很特别。
然后我们发现有个突破口,之前n很大 x = 1,然后很多数字完全不会被访问到,因此省了空间,那这里是不是也可以通过类似的办法省空间呢?
废话,当然可以,突然发现q太小了,才500,撑死500行会发生修改,你只需要开500 * 50000的数组就完事了。
你需要离线处理,然后直接离散一下(记得记录行号之间的映射关系),只存存在修改的那几列就行了,然后最后一列单独拿粗来暴力维护。
整个算法还是暴力的,因此这部分可以跟1 - 6一起做,总复杂度应该是q(n + m),没有压力。
80分很快就到手了,想加写程序都很轻松,1小时不到就完成了,下面贴一下80分的源码。觉得有困难的可以先练练手(注意开long long,还有强转)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <math.h>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <complex>
#define left (now<<1)
#define right ((now<<1)+1)
#define mid ((l + r) >> 1)
#define midmid ((r + mid) >> 1)
#define LONG_LONG_MIN -9223372036854775808ll
#define LONG_LONG_MAX 9223372036854775807ll
using namespace std;
typedef long long int ll;const int MAXN = 3e5 + 10;
struct s1{
int x,y;
};int n,m,q,nn;
queue<ll> qq;
s1 a[MAXN];
int bit[2 * MAXN],len;
ll data[2 * MAXN];
bool flag;
ll g[510][50010];
int pos[50010];int lowbit(int x){
return x & (-x);
}void add(int x,int y){
while(x <= 600000){
bit[x] += y; x += lowbit(x);
}
}int getsum(int x){
int re = 0;
while(x > 0){
re += bit[x]; x -= lowbit(x);
}
return re;
}int main(){
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&q); flag = true;
for(int i = 1; i <= q; ++i){
scanf("%d%d",&a[i].x,&a[i].y);
if(a[i].x != 1){
flag = false;
}
}
if(flag){
for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i){
qq.push(1ll * i * m);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= 600000; ++i){
bit[i] = lowbit(i);
}
len = m;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){
data[i] = i;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= q; ++i){
int l,r; l = 1; r = len;
while(l < r){
if(getsum(mid) >= a[i].y){
r = mid;
}else{
l = mid + 1;
}
}
printf("%lld\n",data[l]); add(l,-1); qq.push(data[l]);
data[++len] = qq.front(); qq.pop();
}}else{
if(q <= 500){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
data[i] = 1ll * m * i;
pos[i] = 0;
}
nn = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= q; ++i){
if(pos[a[i].x] == 0){
pos[a[i].x] = ++nn;
for(int j = 1; j <= m - 1; ++j){
g[nn][j] = 1ll * (a[i].x - 1) * m + j;
}
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= q; ++i){
ll x = a[i].x; ll xx = pos[a[i].x];
if(a[i].y != m){
ll ans = g[xx][a[i].y];
printf("%lld\n",ans);
for(int j = a[i].y; j < m - 1; ++j){
g[xx][j] = g[xx][j + 1];
}
g[xx][m - 1] = data[x];
for(int j = x; j < n; ++j){
data[j] = data[j + 1];
}
data[n] = ans;
}else{
ll ans = data[x];
printf("%lld\n",ans);
for(int j = x; j < n; ++j){
data[j] = data[j + 1];
}
data[n] = ans;
}
}
}else{
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
}
好了,80分到手了,现场的话,1小时T3拿了80还是很舒服的,但是我们现在肯定不满足于只拿80分,剩下20分怎么搞??一般前面的数据点都会对正解有提示性,就跟数学考试,前几问一般会对最后一问有提示性作用。
我们想下刚才整理的思路。
首先最后一列肯定单独拿出来维护,我们发现,这个时候这个最后一列是删一个点,然后尾部插入,这不就是咱们11 - 16的第一行的算法么??
直接拿那部分算法的思路维护这一列就OK了,easy
然后是空间的问题,考虑到我们之前的思路,因为q比起n * m来说,太小太小了,很多点直接仍然是原先的相邻关系,一块一块的。而且之前我们是靠离线处理(预先读入q)来搞一些事,把空间省下来,这里很可能就是类似的办法。
想到这里还算轻松,后面我就想的有点慢了,因为解法不太清晰。
由于每次对某行修改,这一行和最后特别的那一列有互动,除此之外跟其他行根本不会有任何影响。因此考虑,把某一行的操作都单独取出来,看看能不能搞点事。
然后我就立马想到了做法
假设现在都是对第i行操作,一行有m个,操作按顺序为2,2,4
按我们刚才的想法,你去删了2,后面2个操作就变成实际删第3个数,和第5个数,这部分也可以拿树状数组搞诶,跟最后一列是一样的。
那么我们把每一行的操作这样单独取出来,然后算出来它的真实删的第几个数字就好了。
但是还有个很大的问题,如果算出来真实要删的数字大于等于m怎么办???
先想等于m的,等于m的时候,其实就是删最后一列去了。这个时候其实跟这一行木有关系,只跟当前这一列的状态有关,那么直接去这一列上搞事就好了,我们就标记一个flag,表示这个是直接在列上搞事,不需要算真实是删第几个数字。
那么大于m呢(假如是第h个)?显然,删的数字是从那一列第h - (m - 1)次加进来的。
这里我们发现q很小,也就是说对于所有的行来说,加进来的数字不超过q个(其实就是q个),那我们可以拿一个邻接表(vector就很好~)来存第i行后面加进来的数字。
那么我们满分的算法就粗来了,我们总结下。
首先你把所有操作读进来,然后按行排序,同一行按操作先后排序,然后预处理出它真实删除的位置,如果是第m位,flag记一下,不是就算真实位置。
算完以后按编号重新排序,然后我们开始操作。
如果这个操作的y小于m,直接可以算出答案,答案就是(x - 1) * m + y 然后去维护那一列,删掉那一列第x大的数字,丢到vector<x>里,把答案插到那一列末尾
如果这个操作等于m,那么就只在列上搞事就好了,vector也不用丢。
如果大于m,先减去m(vector是从0开始的),答案就是vector[x][m], 然后去维护最后一列,删掉第x大的数字........这部分不重述了
然后就AC啦~~~
这里有个细节,其实这个细节困扰我20,30分钟,我看题解很多人也是用别的办法搞的
就是你预处理每一行的询问的时候,每次树状数组处理完,你都得初始化,初始化的复杂度最坏是n * 3E5,肯定超时。 如果你开n个树状数组,空间必爆
所以题解很多人开了动态加点的线段树,呃
其实这里后来仔细想了想,q不是很少么,每次操作完以后,记一下,你把哪些点单点修改为0了,重新把那些点+1就好了啊、
这里记不能开bool数组记,不然枚举哪些被改了还是要平方复杂度。
搞个vector记就好了。
下面是参考代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <math.h>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <complex>
#define left (now<<1)
#define right ((now<<1)+1)
#define mid ((l + r) >> 1)
#define midmid ((r + mid) >> 1)
#define LONG_LONG_MIN -9223372036854775808ll
#define LONG_LONG_MAX 9223372036854775807ll
using namespace std;
typedef long long int ll;const int MAXN = 3e5 + 10;
struct s1{
int x,y,id;
bool flag;
};vector<ll> v[MAXN];
vector<int> a;
int n,m,q,len,len2,st,ed;
s1 g[MAXN];
ll p[2 * MAXN];
int bit1[2 * MAXN],bit2[2 * MAXN];int lowbit(int x){
return x & (-x);
}void add(int x,int y,int *bit){
while(x <= 600010){
bit[x] += y; x += lowbit(x);
}
}int getsum(int x,int *bit){
int re = 0;
while(x > 0){
re += bit[x]; x -= lowbit(x);
}
return re;
}bool cmp1(s1 x,s1 y){
if(x.x != y.x){
return x.x < y.x;
}else{
return x.id < y.id;
}
}bool cmp2(s1 x,s1 y){
return x.id < y.id;
}int main(){
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&q); len = n;
for(int i = 1; i <= q; ++i){
scanf("%d%d",&g[i].x,&g[i].y);
g[i].id = i; g[i].flag = false;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
p[i] = 1ll * i * m;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= 600010; ++i){
bit1[i] = bit2[i] = lowbit(i);
}
sort(g + 1,g + 1 + q,cmp1); st = 1; ed = 1;
while(st <= q){
while(ed < q && g[st].x == g[ed + 1].x){
++ed;
}
a.clear(); len2 = m;
for(int i = st; i <= ed; ++i){
if(g[i].y == m){
g[i].flag = true; continue;
}
int l = 1,r = len2;
while(l < r){
if(getsum(mid,bit2) >= g[i].y){
r = mid;
}else{
l = mid + 1;
}
}
add(l,-1,bit2); a.push_back(l); g[i].y = l; ++len2;
}
for(int i = 0; i < a.size(); ++i){
add(a[i],1,bit2);
}
st = ed + 1;
}
sort(g + 1,g + 1 + q,cmp2);for(int i = 1; i <= q; ++i){
ll ans;
if(!g[i].flag){
if(g[i].y < m){
ans = 1ll * (g[i].x - 1) * m + g[i].y;
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}else{
g[i].y = g[i].y - m;
ans = v[g[i].x][g[i].y];
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
}int l = 1,r = len;
while(l < r){
if(getsum(mid,bit1) >= g[i].x){
r = mid;
}else{
l = mid + 1;
}
}
add(l,-1,bit1);
if(!g[i].flag){
v[g[i].x].push_back(p[l]);
}else{
ans = p[l];
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
p[++len] = ans;
}
return 0;
} -
1@ 2018-10-30 08:54:26
原文地址:NOIP2017提高组DAY2题解
考察知识:树状数组,平衡树,模拟
算法难度:XXXX+ 实现难度:XXXX+
分析:
我们先分析一下列队的移动:
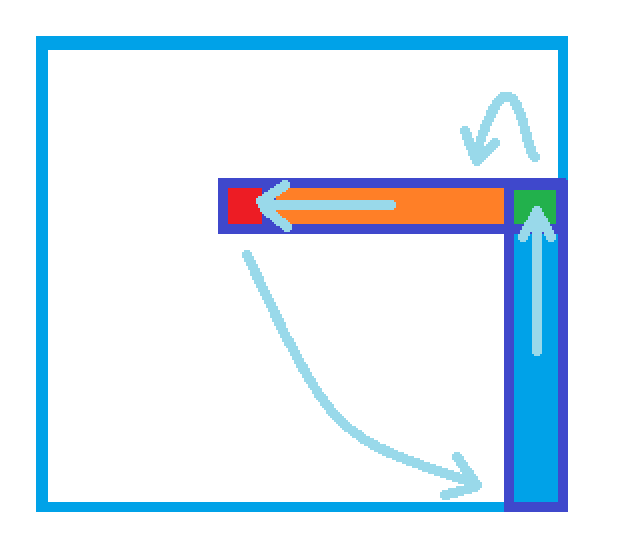
如图,我们发现如果红色那块要出队,共需要移动四块。我们发现种序列的移动可以用Splay来维护,仔细观察发现,水平有n行可能需要移动,而竖直只可能发生在最后一列,所以我们维护 n+1 个Splay,维护n个长度为m-1的序列,1个长度为n的序列。
每次移动时(x,y),我们需要将水平第x个Splay中第y个元素删除,将竖直Splay的第x个元素删除,然后将删除的两个元素分别插入这两个Spaly就可以了。
但是如果我们直接开Splay,空间不够,注意到,我们可以用Spaly维护区间,每次删除时需要将区间一分为三,然后将中间元素删除并更新剩余两个区间。
理解了上面的思路后,剩下的就基本是Spaly的基本操作+变形了,考察大家对Splay的熟练程度了。
注意:
1.最大值会超过int,所以区间用long long储存
2.Spaly常数比较大,可能会有部分点超时。(vijos:可以AC;洛谷:不开O2 95 开O2 AC)
代码:
#include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; #define ll long long const int N=300005,maxn=2400005; int ch[maxn][2],fa[maxn],sz[maxn],now,cnt[maxn]; ll L[maxn],R[maxn]; struct Splay{ int rt; Splay(){rt=0;} int NewNode(ll l,ll r){//新建节点 now++,L[now]=l,R[now]=r; sz[now]=cnt[now]=r-l+1; return now; } void init(ll l,ll r){rt=NewNode(l,r);}//空树的初始化 #define upd(x) cnt[x]=R[x]-L[x]+1 #define pushup(x) sz[x]=sz[ch[x][0]]+sz[ch[x][1]]+cnt[x] #define DB_ for(int i=0;i<=now;i++) \ printf("[%lld,%lld]%d<- %d[%lld,%lld] ->%d[%lld,%lld]\n", \ L[ch[i][0]],R[ch[i][0]],ch[i][0],i,L[i],R[i],ch[i][1],L[ch[i][1]],R[ch[i][1]]);\ puts("----------------") int chk(int x){return x==ch[fa[x]][1];} void rotate(int x){ int y=fa[x],z=fa[y],k=chk(x),w=ch[x][k^1]; ch[y][k]=w,fa[w]=y; ch[z][chk(y)]=x,fa[x]=z; ch[x][k^1]=y,fa[y]=x; pushup(y),pushup(x); } void splay(int x,int goal=0){ while(fa[x]!=goal){ int y=fa[x],z=fa[y]; if(z!=goal){ if(chk(x)==chk(y)) rotate(y); else rotate(x); } rotate(x); } if(!goal) rt=x; } void insert(ll l,ll r){//插入到序列末尾 if(rt==0) {init(l,r);return;} int cur=rt; while(ch[cur][1]) cur=ch[cur][1]; ch[cur][1]=NewNode(l,r),fa[ch[cur][1]]=cur; splay(ch[cur][1]); } int beside(int x,int pre){//求一个子序列的前驱/后继 splay(x); int cur=ch[x][pre^1]; if(!cur) return 0; while(ch[cur][pre]) cur=ch[cur][pre]; return cur; } ll kth_and_del(int k,bool exit_=false){//查找第k大的数并从子序列中删除 int cur=rt; if(sz[rt]==1){//只有一个数 rt=0;//变为空树 return L[cur]; } while(true){//kth if(ch[cur][0]&&k<=sz[ch[cur][0]]) cur=ch[cur][0]; else if(k>sz[ch[cur][0]]+cnt[cur]) k-=sz[ch[cur][0]]+cnt[cur],cur=ch[cur][1]; else break; } k-=sz[ch[cur][0]]; if(exit_) return L[cur]+k-1;//仅查询不删除,用于查看中间结果 int pre=beside(cur,1),nxt=beside(cur,0);//del if(pre) splay(pre); if(nxt) splay(nxt,pre); if(L[cur]==R[cur]){//子序列只有一个数,直接删除 if(nxt) ch[nxt][0]=0;//特别注意!分类讨论不存在前驱或后继的情况 else if(pre) ch[pre][1]=0; else rt=0; if(pre) sz[pre]--; if(nxt) sz[nxt]--; return L[cur]; } else{ ll ret=L[cur]+k-1; if(k==1) L[cur]++,upd(cur),sz[cur]--; else if(k==cnt[cur]) R[cur]--,upd(cur),sz[cur]--; else{//将子序列一分为三,并删除中间的数 ch[cur][0]=NewNode(L[cur],L[cur]+k-2); fa[ch[cur][0]]=cur; L[cur]+=k,upd(cur),pushup(cur); splay(cur); } return ret; } } }s[N]; int n,m,q; void build(){ scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&q); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) s[i].init((ll)(i-1)*m+1,(ll)i*m-1); s[0].init((ll)m,(ll)m); for(int i=2;i<=n;i++) s[0].insert((ll)i*m,(ll)i*m); } void solve(){ int x,y; ll last=(ll)n*m; while(q--){ scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); if(y!=m){ ll t1=s[x].kth_and_del(y),t2=s[0].kth_and_del(x); printf("%lld\n",last=t1); s[x].insert(t2,t2); s[0].insert(t1,t1); } else if(x!=n){ ll t=s[0].kth_and_del(x); printf("%lld\n",last=t); s[0].insert(t,t); }else{ printf("%lld\n",last); } // DB_; //用于查看当前各Splay节点情况 } } int main(){ build(); solve(); return 0; } -
0@ 2021-08-05 09:38:38
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <math.h>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <complex>
#define left (now<<1)
#define right ((now<<1)+1)
#define mid ((l + r) >> 1)
#define midmid ((r + mid) >> 1)
#define LONG_LONG_MIN -9223372036854775808ll
#define LONG_LONG_MAX 9223372036854775807ll
using namespace std;
typedef long long int ll;const int MAXN = 3e5 + 10;
struct s1{
int x,y,id;
bool flag;
};vector<ll> v[MAXN];
vector<int> a;
int n,m,q,len,len2,st,ed;
s1 g[MAXN];
ll p[2 * MAXN];
int bit1[2 * MAXN],bit2[2 * MAXN];int lowbit(int x){
return x & (-x);
}void add(int x,int y,int *bit){
while(x <= 600010){
bit[x] += y; x += lowbit(x);
}
}int getsum(int x,int *bit){
int re = 0;
while(x > 0){
re += bit[x]; x -= lowbit(x);
}
return re;
}bool cmp1(s1 x,s1 y){
if(x.x != y.x){
return x.x < y.x;
}else{
return x.id < y.id;
}
}bool cmp2(s1 x,s1 y){
return x.id < y.id;
}int main(){
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&q); len = n;
for(int i = 1; i <= q; ++i){
scanf("%d%d",&g[i].x,&g[i].y);
g[i].id = i; g[i].flag = false;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
p[i] = 1ll * i * m;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= 600010; ++i){
bit1[i] = bit2[i] = lowbit(i);
}
sort(g + 1,g + 1 + q,cmp1); st = 1; ed = 1;
while(st <= q){
while(ed < q && g[st].x == g[ed + 1].x){
++ed;
}
a.clear(); len2 = m;
for(int i = st; i <= ed; ++i){
if(g[i].y == m){
g[i].flag = true; continue;
}
int l = 1,r = len2;
while(l < r){
if(getsum(mid,bit2) >= g[i].y){
r = mid;
}else{
l = mid + 1;
}
}
add(l,-1,bit2); a.push_back(l); g[i].y = l; ++len2;
}
for(int i = 0; i < a.size(); ++i){
add(a[i],1,bit2);
}
st = ed + 1;
}
sort(g + 1,g + 1 + q,cmp2);for(int i = 1; i <= q; ++i){
ll ans;
if(!g[i].flag){
if(g[i].y < m){
ans = 1ll * (g[i].x - 1) * m + g[i].y;
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}else{
g[i].y = g[i].y - m;
ans = v[g[i].x][g[i].y];
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
}int l = 1,r = len;
while(l < r){
if(getsum(mid,bit1) >= g[i].x){
r = mid;
}else{
l = mid + 1;
}
}
add(l,-1,bit1);
if(!g[i].flag){
v[g[i].x].push_back(p[l]);
}else{
ans = p[l];
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
p[++len] = ans;
}
return 0;
}
- 1
信息
- ID
- 2033
- 难度
- 6
- 分类
- (无)
- 标签
- 递交数
- 255
- 已通过
- 64
- 通过率
- 25%
- 被复制
- 10
- 上传者